Data at Rest encompasses all types of data stored by the system. This will typically include databases, files, emails, etc. A key Data at Rest service is Record Storage that is used to replace the traditional siloed approach to storing data in disparate applications.
DAS Record Storage Service
- This is the core service area and must always be available to other services
- Contains the business record data and is the ultimate target for attacks
- Needs to be isolated from external threats and protected by layered defenses
- All data is encrypted at rest and during transport to other service areas
- Backed up to secure vaults
- Only accessible to authenticated and authorized users
- Can optimize performance for both storage and retrieval using CQRS best practices
- Easy to extend the basic Create, Read, Update and Delete (CRUD) with new capabilities
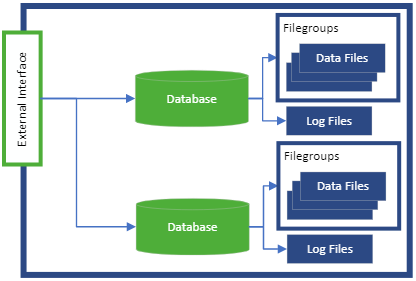
- Data at Rest implementation is completely hidden behind the External Interface from all other services
- No other service component can access the underlying data storage
- Storage can be scaled vertically and horizontally
- Storage can be upgraded or replaced without impacting any other service
How to Make Record STorage Data Agnostic
- In a traditional database design, there is a set of tables and each table contains a set of records. In a DAS Architecture implementation, tables are replaced by “Concepts” and records are replaced by “Instances“
- A Concept is implemented as a data-driven Form Definition that defines the user experience:
- How the data content of the Instance should be interpreted and presented to the user
- The life-cycle of the Instance expressed as a State Transition Diagram
- All records are stored in a data agnostic Instances table
- Each Instance can have multiple data elements that can be passed and stored agnostically, for example, using XML or JSON
- Can add complex user-defined field types for compound fields such as addresses
- Each Instance also has meta-data that describes the record
- Each Instance can have multiple data elements that can be passed and stored agnostically, for example, using XML or JSON
- Focus all CRUD (Create, Read, Update and Delete) through a data agnostic Instances table using XML or JSON fields
- Minimalist interface to improve performance and allow different scalability models
- Using XML/JSON allows for “complex” data representations
- Not limited to simple data fields used by table columns in relational databases
- Add metadata to optimize record retrieval
- Enforce security checks and monitoring on all Read/Write requests
- Need only a few simple stored procedures:
- Save Instance – combines Create and Update functionality required to persist records into storage.
- Read Instance – restricts reading the data to users with appropriate access rights.
- Delete Instance – allows for logical deletion of records so that audit trails can be maintained.
- List Instances – returns a list of Instances that match a set of search parameters
- Use a hybrid approach of a Relational database to manage Document data – the best of both worlds!
Go Beyond Basic CRUD to “CRUD+”
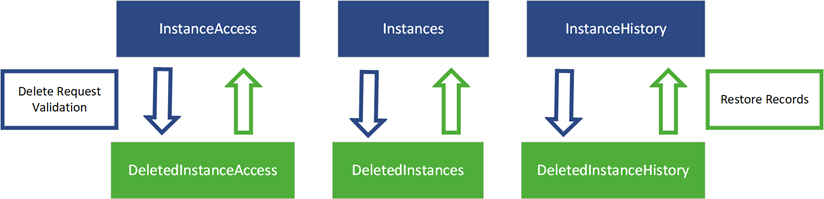
- Only keep the latest version in the Instances table and maintain all versions of each Instance in the InstanceHistory table
- Maintain parent-child hierarchy relationships in the Instances table
- Maintain row-level access control list for each Instance in InstanceAccess table
- Instances can be virtually deleted by moving to “Deleted” tables
- Understanding parent-child relationships also allows for cascaded deletes
- Delete is blocked entirely if the user is not allowed to delete one of the child instances
- Deleted Instances can also be restored as a set
- Can add a policy that permanently archives or removes these logically deleted records based on the business needs.
- Understanding parent-child relationships also allows for cascaded deletes
- Need to optimize data for retrieval as shredding XML or JSON can be very slow
- Can create a trigger on the Instances table to:
- Create multi-level read-only lookup tables to optimize searches
- Copy changes to Reporting or Analytics databases
- Initiate live data transfers to 3rd party applications
- Add indexes on lookup tables to optimize search performance
- Can create a trigger on the Instances table to:
What makes Data At Rest Record Storage Sustainable?
- Record data is just stored as XML/JSON within an Instance which makes it easy to:
- Add/remove elements from Concepts
- Add/remove whole Concepts
- Restructure how Concepts inter-relate
- Reuse Concepts in multiple places in the data model
- Extend the CRUD+ functionality as new requirements emerge
- Migrate existing data from legacy applications
- Implementation is hidden behind the external interface which makes it easy to:
- Replace/upgrade underlying technology
- Use the Instance/Concept information to partition across multiple servers/databases/disks
- Replicate incoming data to multiple databases (OLTP/OLAP/Reporting/Cloud Analytics)
- Onboard new resources quickly
- Architecture and infrastructure is simple and easy to understand
- Do not need to understand a complex relational data model
- Can optimize read-only lookup tables and queries individually

